

Which three conditions can cause excessive unicast flooding? (Choose three.)
Correct Answer:
ABE
🗳️
Causes of Flooding -
The very cause of flooding is that destination MAC address of the packet is not in the L2 forwarding table of the switch. In this case the packet will be flooded out of all forwarding ports in its VLAN (except the port it was received on). Below case studies display most common reasons for destination MAC address not being known to the switch.
"Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - www.actualtests.com 4
Cause 1: Asymmetric Routing -
Large amounts of flooded traffic might saturate low-bandwidth links causing network performance issues or complete connectivity outage to devices connected across such low-bandwidth links.
Cause 2: Spanning-Tree Protocol Topology Changes
Another common issue caused by flooding is Spanning-Tree Protocol (STP) Topology Change Notification (TCN). TCN is designed to correct forwarding tables after the forwarding topology has changed. This is necessary to avoid a connectivity outage, as after a topology change some destinations previously accessible via particular ports might become accessible via different ports. TCN operates by shortening the forwarding table aging time, such that if the address is not relearned, it will age out and flooding will occur.
TCNs are triggered by a port that is transitioning to or from the forwarding state. After the TCN, even if the particular destination MAC address has aged out, flooding should not happen for long in most cases since the address will be relearned. The issue might arise when TCNs are occurring repeatedly with short intervals. The switches will constantly be fast-aging their forwarding tables so flooding will be nearly constant.
Normally, a TCN is rare in a well-configured network. When the port on a switch goes up or down, there is eventually a TCN once the STP state of the port is changing to or from forwarding. When the port is flapping, repetitive TCNs and flooding occurs.
Cause 3: Forwarding Table Overflow
Another possible cause of flooding can be overflow of the switch forwarding table. In this case, new addresses cannot be learned and packets destined to such addresses are flooded until some space becomes available in the forwarding table. New addresses will then be learned. This is possible but rare, since most modern switches have large enough forwarding tables to accommodate MAC addresses for most designs.
Forwarding table exhaustion can also be caused by an attack on the network where one host starts generating frames each sourced with different MAC address.
This will tie up all the forwarding table resources. Once the forwarding tables become saturated, other traffic will be flooded because new learning cannot occur.
This kind of attack can be detected by examining the switch forwarding table. Most of the MAC addresses will point to the same port or group of ports. Such attacks can be prevented by limiting the number of MAC addresses learned on untrusted ports by using the port security feature.
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/switches/catalyst-6000-series- switches/23563-143.html#causes
Which congestion-avoidance or congestion-management technique can cause global synchronization?
"Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - www.actualtests.com 5
Correct Answer:
A
🗳️
Tail Drop -
Tail drop treats all traffic equally and does not differentiate between classes of service. Queues fill during periods of congestion. When the output queue is full and tail drop is in effect, packets are dropped until the congestion is eliminated and the queue is no longer full.
Weighted Random Early Detection -
WRED avoids the globalization problems that occur when tail drop is used as the congestion avoidance mechanism on the router. Global synchronization occurs as waves of congestion crest only to be followed by troughs during which the transmission link is not fully utilized. Global synchronization of TCP hosts, for example, can occur because packets are dropped all at once. Global synchronization manifests when multiple TCP hosts reduce their transmission rates in response to packet dropping, then increase their transmission rates once again when the congestion is reduced.
Reference:
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios/12_2/qos/configuration/guide/fqos_c/qcfconav.html#wp1 002048
Refer to the exhibit.
Which statement about the output is true?
Correct Answer:
A
🗳️
We can see that the connection is initiated by the Source IP address shown as 144.254.10.206. We also see that the destination protocol (DstP) shows 01BB, which is in hex and translates to 443 in decimal. SSL/HTTPS uses port 443.
"Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - www.actualtests.com 9
What is the cause of ignores and overruns on an interface, when the overall traffic rate of the interface is low?
Correct Answer:
D
🗳️
Micro-bursting is a phenomenon where rapid bursts of data packets are sent in quick succession, leading to periods of full line-rate transmission that can overflow packet buffers of the network stack, both in network endpoints and routers and switches inside the network. Symptoms of micro bursts will manifest in the form of ignores and/ or overruns (also shown as accumulated in "input error" counter within show interface output). This is indicative of receive ring and corresponding packet buffer being overwhelmed due to data bursts coming in over extremely short period of time (microseconds). You will never see a sustained data traffic within show interface's "input rate" counter as they are averaging bits per second (bps) over 5 minutes by default (way too long to account for microbursts). You can understand microbursts from a scenario where a 3-lane highway merging into a single lane at rush hour the capacity burst cannot exceed the total available bandwidth (i.e. single lane), but it can saturate it for a period of time.
Reference: http://ccieordie.com/?tag=micro-burst
Which implementation can cause packet loss when the network includes asymmetric routing paths?
Correct Answer:
C
🗳️
When administrators use Unicast RPF in strict mode, the packet must be received on the interface that the router would use to forward the return packet. Unicast
RPF configured in strict mode may drop legitimate traffic that is received on an interface that was not the router's choice for sending return traffic. Dropping this legitimate traffic could occur when asymmetric routing paths are present in the network.
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/web/about/security/intelligence/unicast-rpf.html
Which two mechanisms can be used to eliminate Cisco Express Forwarding polarization? (Choose two.)
Correct Answer:
BD
🗳️
This document describes how Cisco Express Forwarding (CEF) polarization can cause suboptimal use of redundant paths to a destination network. CEF polarization is the effect when a hash algorithm chooses a particular path and the redundant paths remain completely unused.
How to Avoid CEF Polarization -
The hash algorithm load-balances this way by default:
1: 1
2: 7-8
3: 1-1-1
4: 1-1-1-2
5: 1-1-1-1-1
6: 1-2-2-2-2-2
"Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - www.actualtests.com 13
7: 1-1-1-1-1-1-1
8: 1-1-1-2-2-2-2-2
The number before the colon represents the number of equal-cost paths. The number after the colon represents the proportion of traffic which is forwarded per path.
This means that:
This illustrates that, when there is even number of ECMP links, the traffic is not load-balanced.
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/ip/express-forwarding-cef/116376- technote-cef-00.html
Which two mechanisms provide Cisco IOS XE Software with control plane and data plane separation? (Choose two.)
Correct Answer:
AB
🗳️
Control Plane and Data Plane Separation
IOS XE introduces an opportunity to enable teams to now build drivers for new Data Plane ASICs outside the IOS instance and have them program to a set of standard APIs which in turn enforces Control Plane and Data Plane processing separation.
IOS XE accomplishes Control Plane / Data Plane separation through the introduction of the Forwarding and Feature Manager (FFM) and its standard interface to the Forwarding Engine Driver (FED). FFM provides a set of APIs to Control Plane processes. In turn, the FFM programs the Data Plane via the FED and maintains forwarding state for the system. The FED is the instantiation of the hardware driver for the Data Plane and is provided by the platform.
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/ios-nx-os-software/ios-xe- 3sg/QA_C67-622903.html
"Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - www.actualtests.com 14
Refer to the exhibit.
What is the PHB class on this flow?
Correct Answer:
D
🗳️
This command shows the TOS value in hex, which is 80 in this case. The following chart shows some common DSCP/PHB Class values:
Service -
DSCP value -
TOS value -
Juniper Alias -
TOS hexadecimal -
DSCP - TOS Binary -
Premium IP -
ef
B8 -
101110 - 101110xx
LBE -
cs1
001000 - 001000xx
"Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - www.actualtests.com 15
DWS -
cs4
100000 - 100000xx
Network control -
cs6
c0
110000 - 110000xx
Network control 2 -
cs7
e0
111000 - 111000xx
Reference: http://www.tucny.com/Home/dscp-tos
Refer to the exhibit.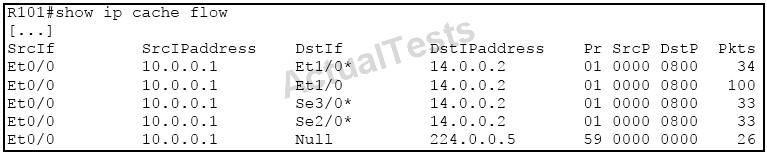
What kind of load balancing is done on this router?
Correct Answer:
A
🗳️
"Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - www.actualtests.com 16
Here we can see that for the same traffic source/destination pair of 10.0.0.1 to 14.0.0.2 there were a total of 100 packets (shown by second entry without the *) and that the packets were distributed evenly across the three different outgoing interfaces (34, 33, 33 packets, respectively.
What is the most efficient way to confirm whether microbursts of traffic are occurring?
Correct Answer:
D
🗳️
Micro-bursting is a phenomenon where rapid bursts of data packets are sent in quick succession, leading to periods of full line-rate transmission that can overflow packet buffers of the network stack, both in network endpoints and routers and switches inside the network. In order to troubleshoot microbursts, you need a packet sniffer that can capture traffic over a long period of time and allow you to analyze it in the form of a graph which displays the saturation points (packet rate during microbursts versus total available bandwidth). You can eventually trace it to the source causing the bursts (e.g. stock trading applications).
Reference: Adam, Paul (2014-07-12). All-in-One CCIE V5 Written Exam Guide (Kindle Locations 989-994). Kindle Edition.