

Refer to the exhibit.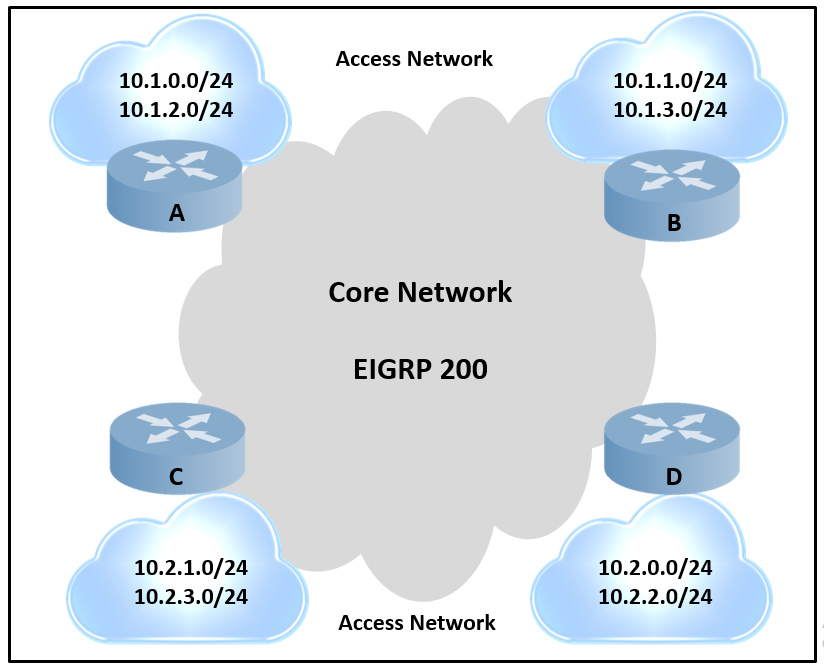
An engineer is designing a routing solution for a customer. The design must ensure that a failure of network 10.1.0.0/24, 10.1.2.0/24, 10.2.1.0/24, or 10.2.3.0/24 does not impact the core. It also requires fast convergence time during any link failover in the core or access networks.
Which solution must the engineer select?
khazbimoas
1 month agowolfone
4 months, 1 week agowolfone
4 months, 1 week ago26d13e9
8 months, 1 week agoClauster
1 year, 5 months agoEmily23
1 year, 6 months agoKacein
8 months, 1 week agoSpicyMochi
1 year, 8 months agocerifyme85
1 year, 9 months ago